low end tidal co2 pulmonary embolism
Arterial to end-tidal CO2 gradient as an indicator of silent pulmonary embolism. In 12 patients with massive pulmonary embolism who required mechanical ventilation mean pulmonary arterial pressure MPAP and end-tidal carbon dioxide tension ETCO2 were registered continuously during thrombolytic therapy.

Different Capnography Traces A Sudden Drop In E 0 Co2 B Download Scientific Diagram
The mission of The Annals of Thoracic Surgery is to promote scholarship in cardiothoracic surgery patient care.

. End-tidal carbon dioxide tension P ETCO 2 is a physiological surrogate for vascular obstruction from PE. Massive pulmonary embolism PE results in low CO 2 transport due to hemodynamic compromise together with an alveolar dead space effect increase in poorly perfused but well ventilated lung areas. A non-randomized single center prospective descriptive correlational design was used to determine what end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO 2 level provided the best sensitivity specificity and negative predictive value to exclude pulmonary embolism PE diagnosis in hemodynamically stable hospitalized adults n 111.
The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism PE because of nonspecific clinical presentation remains as a challenge for emergency physicians. Pulmonary embolism increases alveolar dead space resulting in low end-tidal CO 2 EtCO 2 relative to arterial CO 2 PaCO 2 tension. Pulmonary thromboembolism results in dead space ventilation and therefore prevents meaningful gas exchange in the subtended lung unit yielding an alveolar CO 2 content as low as 0.
1 It is caused by entrapment of carbon dioxide in an injured vein artery or solid organ and results in blockage of the right ventricle RV or pulmonary artery. The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism is often missed. Ad Get Info On An Rx Option To Treat Lower The Risk Of Recurrent DVTPE Blood Clots.
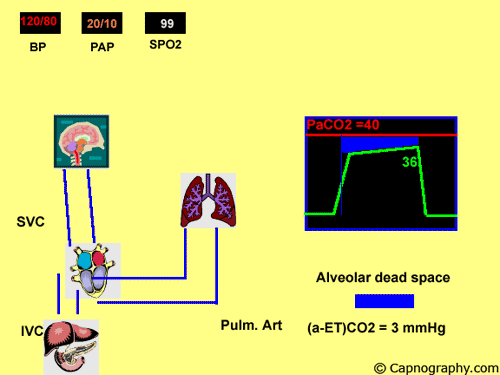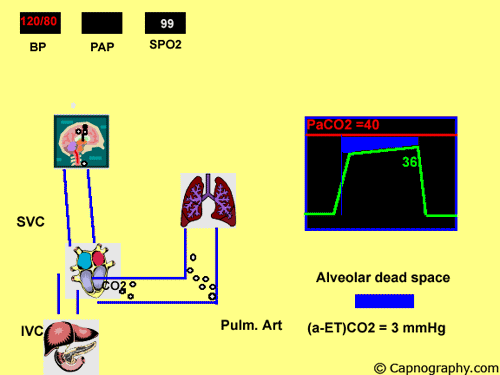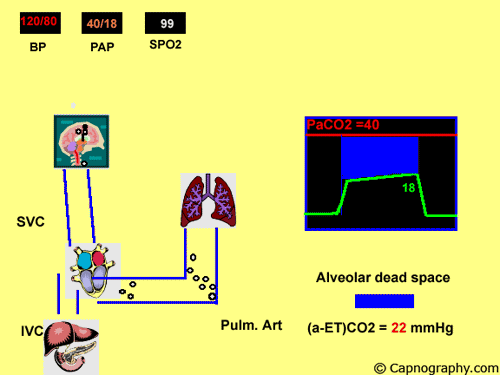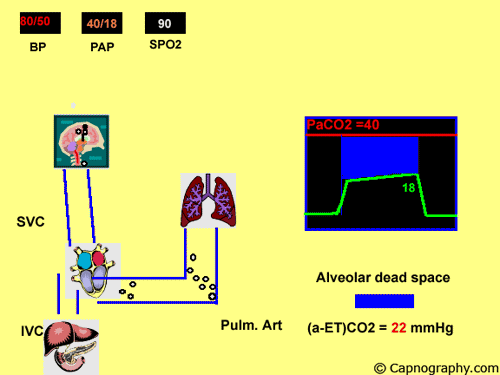
Arterial to end-tidal CO2 gradient as an indicator of silent pulmonary embolism Lancet. Normal PaCO 2 -EtCO 2 difference is 2-5 mmHg Satoh et al 2015 This is due to alveolar dead space which is small in healthy adults. Several studies have reported that computed tomography pulmonary angiography is the best method for diagnosing pulmonary embolism PE.
All study participants underwent end-tidal CO 2 determination within 24 h of state-of-the-art diagnostic imaging. Thus a low EtCO 2 PaCO 2 ratio during resuscitation may be a sign of pulmonary embolism. This study however aimed to predict or exclude PE using the end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 value and alveolar dead space fraction AVDSf together.
Thus a low EtCO 2 PaCO 2 ratio during resuscitation may be a sign of pulmonary embolism. At a cut-off of 36 mmHg capnography achieved a negative predictive value of 966. Alveolar dead space contain a gas mixture which is identical to.
Low end tidal co2 pulmonary embolism Friday 11 February 2022 Edit. Trending this is reasonable but its not entirely reliable. This may result from such ventilatory problems as high mean airway pressure or inadequate exhalation time resulting in overdistention or from such circulatory problems as.
In thromboembolism ETCO2 is significantly lower than normal due to the reduction of pulmonary perfusion and increased alveolar dead space that reduces the amount of CO2 exhaled from the lungs so venous carbon dioxide pressure PvCO2 increases and all of these changes lead to an increase in arterial CO2-ETCO2 gradient. The financial impact and harm avoidance of adding EtCO 2. Visit The Official Patient Site For Additional Information About DVTPE Blood Clots.
End tidal CO2 is reduced during hypotension and cardiac arrest. Arterial to end-tidal partial pressure of carbon dioxide Pa-Et CO 2 gradient may be useful in the evaluation of PE. The authors aimed to define the optimum ETCO 2 to conclusively exclude a pulmonary embolic event.
Carbon dioxide embolism is a rare but potentially serious complication of laparoscopic procedures. Authors S Taniguchi K. Post hoc analysis of data from two porcine studies comparing.
Dead-space ventilation results in ventilated alveoli with insufficient perfusion which leads to low ETco 2. If there was no alveolar dead space end-tidal CO 2 would be identical to alveolar CO 2. A low end-tidal CO2arterial CO2 ratio during cardiopulmonary resuscitation suggests pulmonary embolism.
Cardiac arrest from PE is associated with extremely low etCO2 readings during CPR. End-tidal CO 2 ETCO 2 can represent dead space ventilation. One hundred consecutive patients with suspected pulmonary embolisms PEs were enrolled over 6 months in 2012.
Pulmonary embolism increases alveolar dead space resulting in low end-tidal CO 2 EtCO 2 relative to arterial CO 2 PaCO 2 tension. A DVT Is A Blood Clot Which Can Travel To The Lungs And Lead To A PE. At the third rhythm analysis EtCO 2 levels were significantly lower when cardiac arrest was caused by pulmonary embolism.
The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism is often missed. In the group of patients finally diagnosed with PE n 39 end-tidal CO 2 was significantly lower than in the group without PE or in healthy volunteers. PaCO2 cardiac index as estimated by thermodilution catheter and respiratory ratio of arterial oxygen tension and inhaled oxygen.
2 There have been reports of carbon dioxide emboli occurring in various procedures including laparoscopic. Alveoli which are ventilated but not perfused ie. Ad Get The Facts About Deep Vein Thrombosis Pulmonary Embolism Discover Common Symptoms.
End-tidal clearance must be evaluated in the context of the patients perfusion status. Volume 133 December 2018 Pages 137-140 December 2018 Pages 137-140.

A Low End Tidal Co2 Arterial Co2 Ratio During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Suggests Pulmonary Embolism Resuscitation

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Evaluation Of Suspected Pulmonary Embolism Utilizing End Tidal Co2 And D Dimer The American Journal Of Surgery

Pulmonary Embolism Alters Alveolar Dead Space And End Tidal Carbon Download Scientific Diagram

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog
5 Medical Conditions Where Capnography Can Affect Bls Care Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

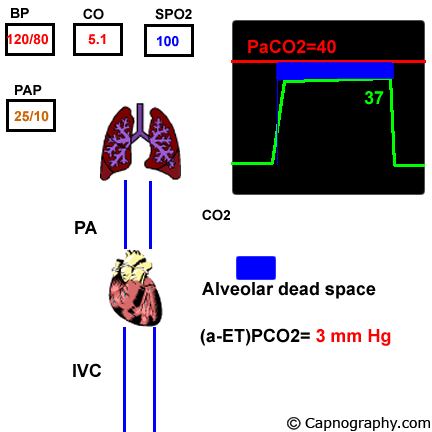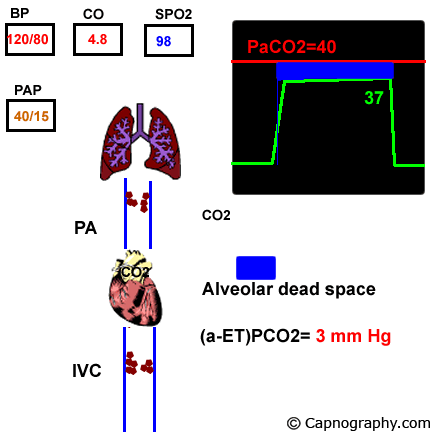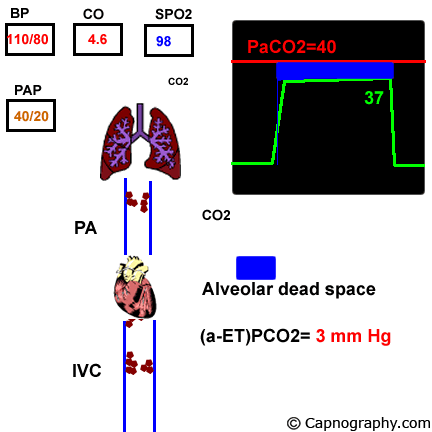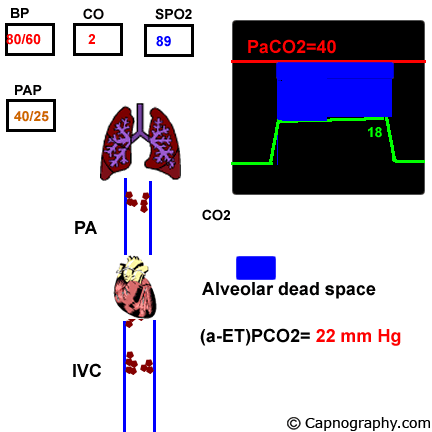
Pulmonary Thrombo Embolism Capnography

Capnography Welcome To Jeremy Jaramillo S Blog
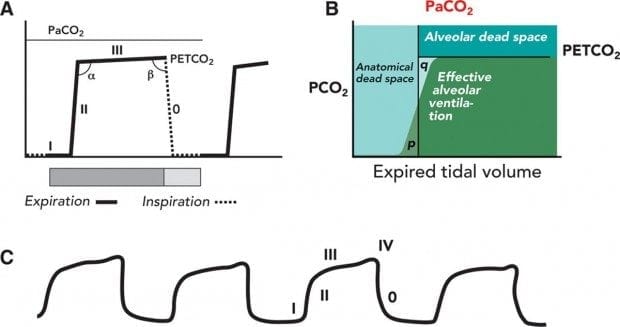
Capnography Waveform Interpretation Litfl Ccc Equipment

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Pulmonary Embolism Alters Alveolar Dead Space And End Tidal Carbon Download Scientific Diagram

A Low End Tidal Co2 Arterial Co2 Ratio During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Suggests Pulmonary Embolism Resuscitation